Planning & design
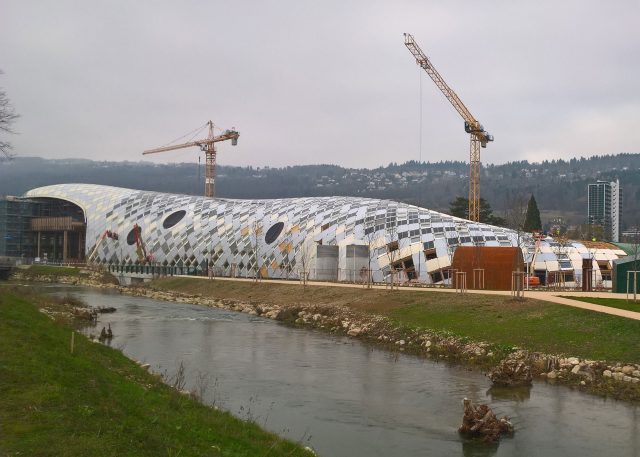
The basic structure of the building consists of glued laminated timber trusses arranged in a grid to depict the organic form of a snake curled up on the ground. The bonded wood structure forms the supporting frame.
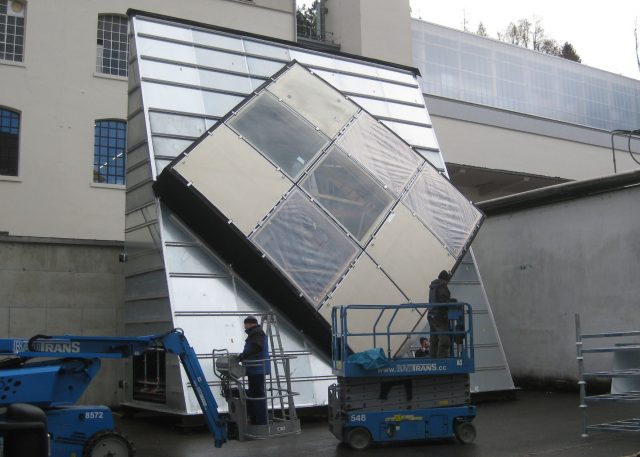
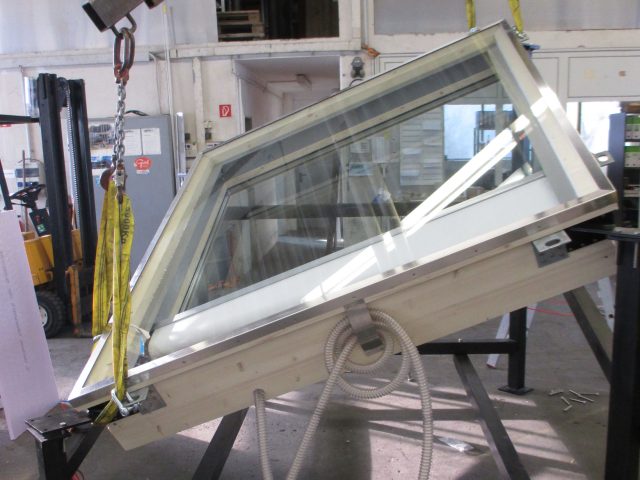
The diamond-shaped openings produced by the primary supporting structure are enclosed by a wide variety of fill elements. The fillings are designed as bent elements due to the curved shape of the building. The respective element types are selected on the basis of differing requirements in terms of the function of the final building envelope.
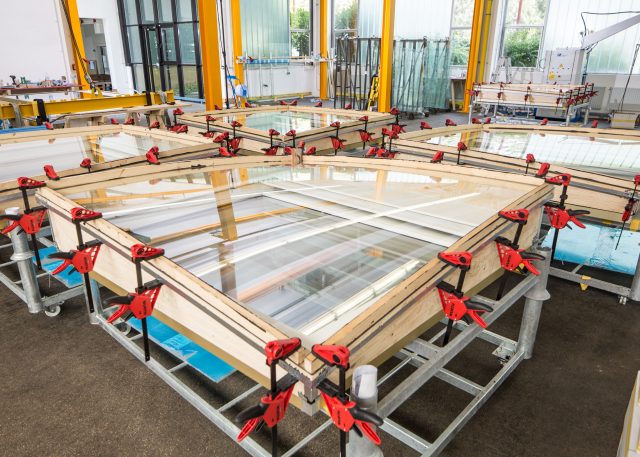
Four distinctive element types are used in order to cater for the high requirements in terms of heat insulation, noise insulation, solar shading and design. These consist mostly of a timber frame which is curved or a rounded/3D milled timber frame in varying shapes. This produces 2,800 facade elements in different geometric shapes with the following superstructures, among others:
- Closed Cavity facade (CCF) elements consisting of internal flat triple insulating glass with a heat insulation layer, external curved single glazing and centrally mounted trapezoidal solar shading countertension system in the space between. The elements are provided with a permanent supply of flushing air to ensure the targeted feed and discharge of dried air in the gap and thus avoid a build-up of condensation.
- ETFE cushion elements comprising opaque and transparent ETFE films with a curved polycarbonate plate and multiple web plates in the gap. The cushions are designed in multiple layers and likewise flushed with air.
Some elements are also configured with photovoltaic technology.
The selection of the right type of timber and the determination of the perfect timber drying stage in particular played a key role in the functionality of the facade elements.